Bolt Stresses
A study into the stresses induced in the mounting bolts was carried out to ascertain their safety. The assumptions made and loading conditions are listed below.
FEA Analysis Assumptions and Conditions
- Boundary Conditions: 4 Positions fixed at each mounting location (Fig.1)
- Axis Orientation: Figures 2, 3
- Bolt preload is not taken into account
- Loading Conditions: Proof loads as per GMRT 2100
- Analysis: Linear Static
- Weight of Model: 170.6N
- Reaction Force has units of N
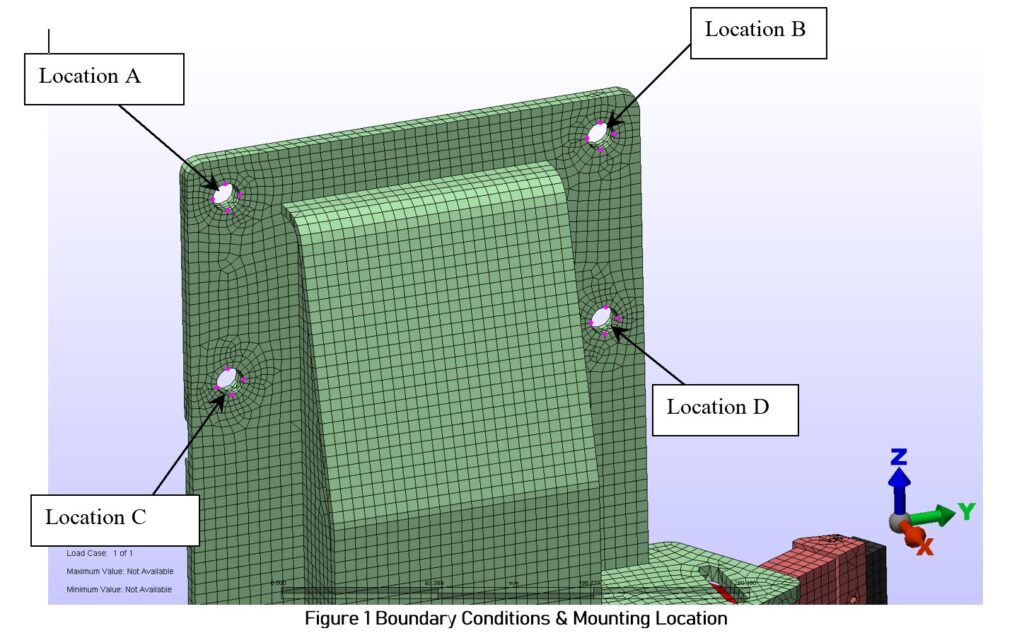
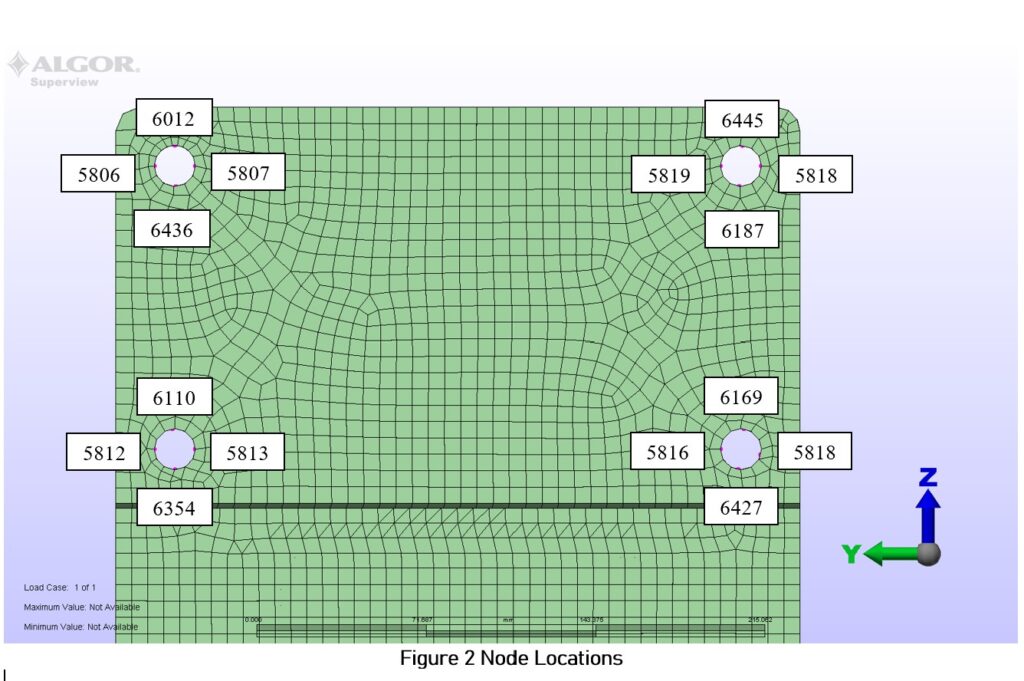
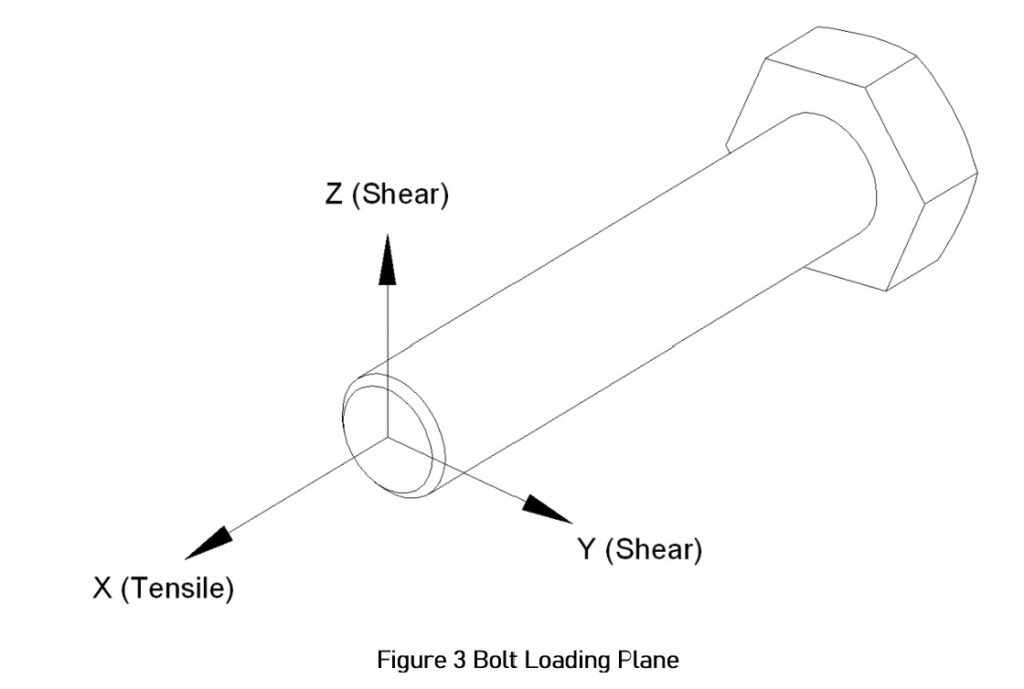
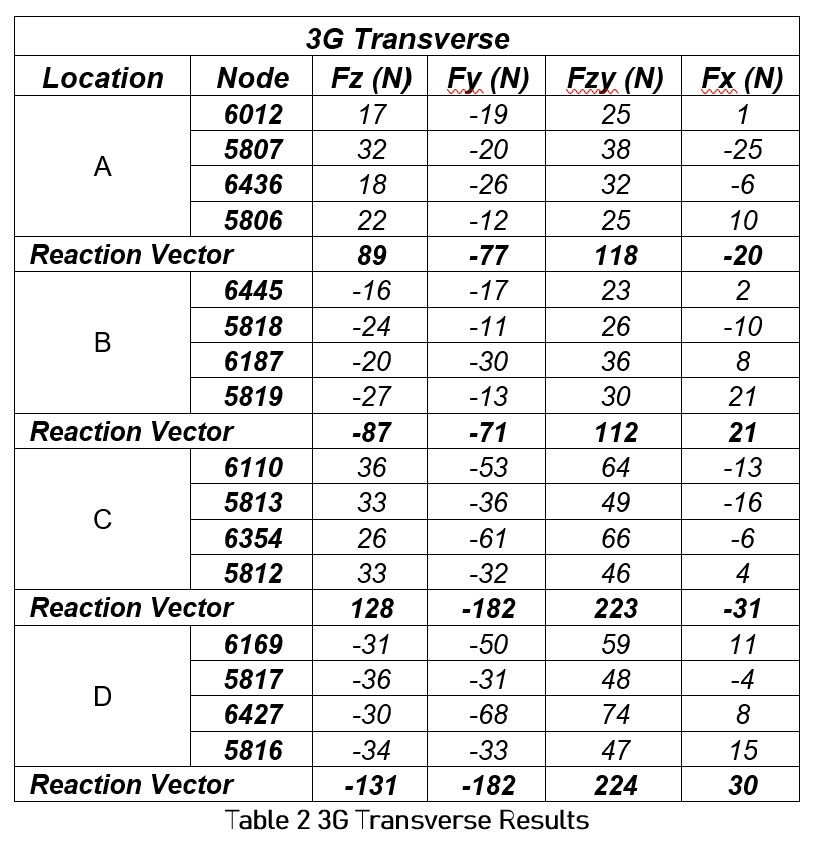
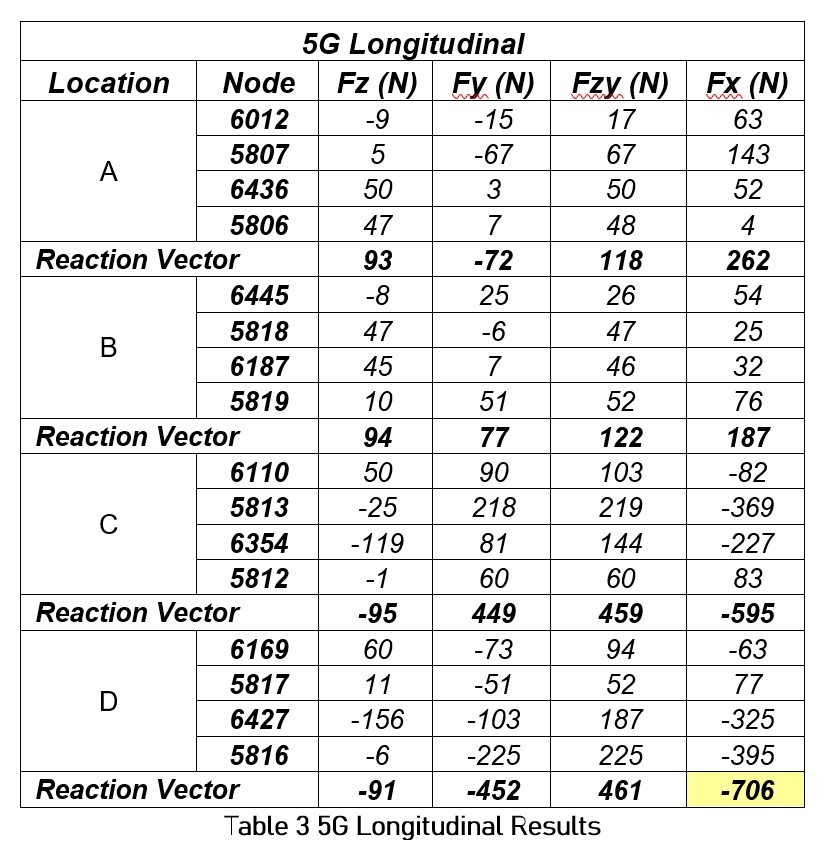
FEA Reaction Results
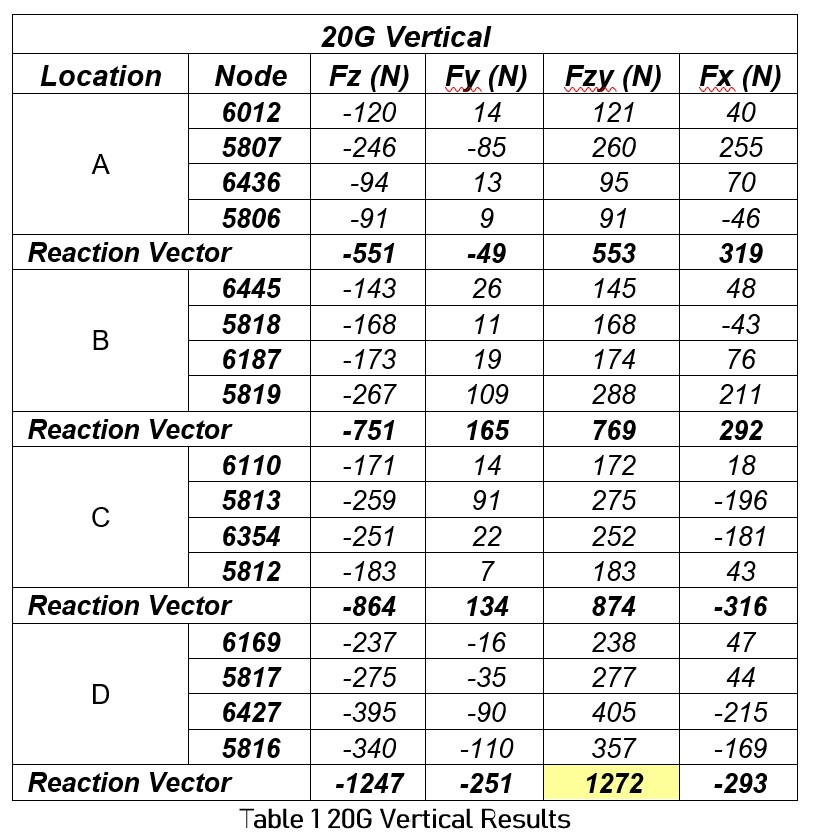
The reaction forces in the X, Y, and Z directions at each of the four nodes associated with the four locations are listed below in Tables 1, 2, and 3. The maximum reaction vector for each loading scenario is highlighted. The FZ and FY force components were summed to find their resultant (FZY) as both contribute to a shear force. The FX value represents the tensile load.
BS 5950-1:2000 Structural use of steelwork in building – Part 1: Code of practice for design- Rolled and welded sections, section 6.3.[5] was referenced to calculate shear and tensile capacities of the bolts.
Section 6.3.2.1 states shear capacity as:
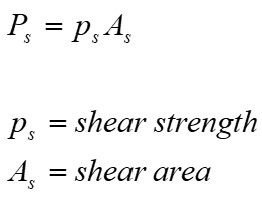
The shear strength, ps, for a Grade 8.8 fastening is stated as 375N/mm2 (Table 30 [5]). However, as the fastenings we are using are stainless steel this value may not be valid. A conservative method of calculating shear strength for a material is 0.4xTensile Strength. The UTS for Grade 8.8 stainless steel is listed as 800N/mm2 [6], therefore a value of 320N/mm2 will be used. The shear area was found in the bottom table of [7]. Therefore:![]()
The shear force (Fs) per bolt must not exceed the shear capacity. FEA results obtained suggest location D under a 20G load created the largest shear force (highlighted, Table 8). Therefore:![]() Section 6.3.4.2 [5] states nominal tension capacity as:
Section 6.3.4.2 [5] states nominal tension capacity as:
The tensile stress area At was obtained from [7], the tension strength found in Table 34 [5] is listed as 560N/mm2. However, as before, because this is a stainless steel fastening this value has been re-evaluated to 0.6xTensile Strength to ensure the most conservative values possible are calculated. Therefore a value of 480N/mm2 will be used.
This results in:![]()
The tensile force (Ft) per bolt must not exceed the nominal tension capacity. FEA results suggest location D under 5G load created the largest tensile force (highlighted, Table 10).
Therefore:![]()
It is also possible to estimate the combined effects of shear and tension using the below relationship (6.3.4.4) [5]: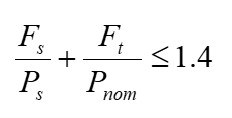
In this case both Fs and Ft must come from the same location. Location D @ 20g will be considered: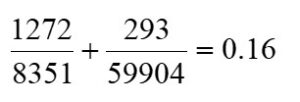
Therefore, the worst case considering combined both shear and tension still equates to a safety factor of 8.75. It is clear from the above calculations that the stresses experienced by the mounting bolts are not of concern.
Conclusions
- The bracket design, under the conditions and assumptions made in the FEA analysis, met all the requirements for proof and fatigue loading in accordance with GM/RT2100.
- Modal analysis reveals that the bracket has a fundamental frequency of 1Hz. Dynamic stresses due to resonance are at acceptable values and no damage or failure is expected to occur.
- The bolt stress calculations suggest the M16x55 Grade 8.8 Stainless Steel bolts recommended for the design are of sufficient size and number to comfortably withstand the loads imparted on them by the structure.
References
1. http://www.efunda.com/materials/alloys/stainless_steels/show_stainless.cfmID=AISI_Type_304&prop=all&Page_Title=AISI%20Type%20304
2.http://www.efunda.com/materials/alloys/carbon_steels/show_carbon.cfm?ID=AISI_1020&prop=all&Page_Title=AISI%201020
3. Railway Group Standard, “GM/RT2100”, Issue 3, October 2000
4.BS7608:1993 Code of practice for fatigue design and assessment of steel Structures
5.BS 5950-1 :2000 Structural use of steelwork in building – Part 1: Code of practice for design- Rolled and welded sections, section 6.3.4
6. http://www.roymech.co.uk/Useful_Tables/Screws/Strength.htm
7. http://www.roymech.co.uk/Useful_Tables/Screws/Thread_Calcs.html
